Current Business Context
Geopolitical power imbalances such as the Russia-Ukraine war, Gaza and Israel conflicts, and Middle East tensions have brought shocks on long-term business growth prospects and created a turbulent business economic environment. Social unrest has further impacted business security and created a negative outlook on today's business growth.
The Global Risks Report has highlighted extreme weather events, critical changes to Earth systems, biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapses as the top three global concerns anticipated over the next 10 years (Global Risks Report, 2024). These key concerns will lead to increases in supply chain risk, consumer risk, and credit risk.
Persistently elevated inflation in many countries and high interest rates are weighing heavily on economic growth. A visible economic downturn with a risk of new economic shocks would be an unmanageable tipping point of sustainability. These factors have created a dilemma for business leaders seeking sustainable business growth prospects.
Sustainable Business Growth
"Our Common Future," also known as the "Brundtland Report" published by The United Nations in 1987, emphasized sustainability as the development which meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs (Brundtland, 1987).
In other words, "you can have your share or your wellbeing, but you should leave enough for others as well."
Sustainability should create a blend and balance between economic, social, and environmental goals. It should comprise financial sustainability (profit), social sustainability (people), and environmental sustainability (planet) — creating the Triple Bottom Line (TBL) (Virakul, 2015).
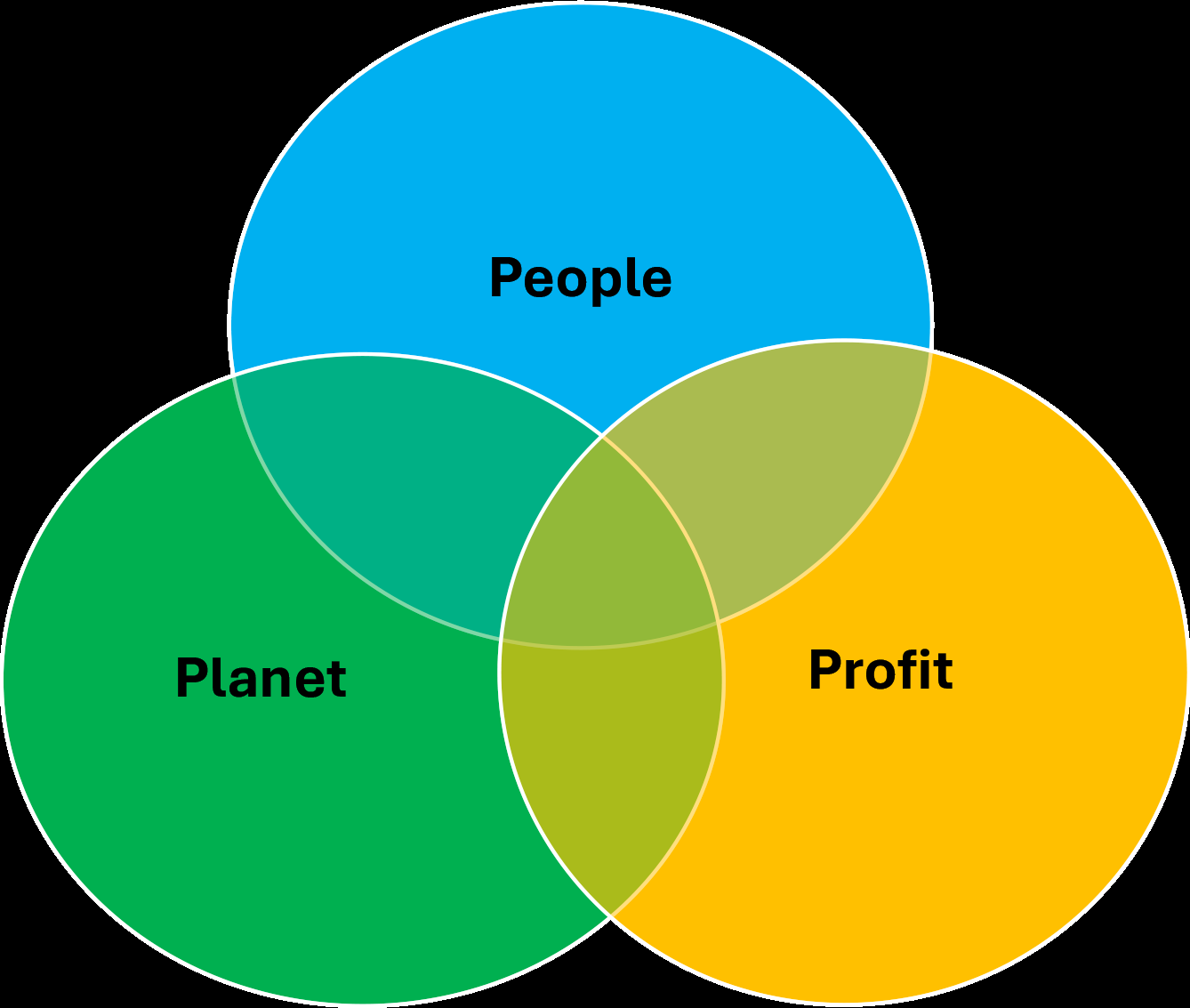
Sustainable business growth emphasizes the process of expanding a business with economic, social, and environmental considerations over the long term. All aspects — social, economic, and environmental — are equally important in sustainable development. But in practice, these aspects have been operationalized in an isolated manner from each other over the last few decades.
The business should balance profitability with positive impacts on society and the environment. It should focus on developing environmental and social dimensions in addition to the traditional measures of profits.
Leadership Challenges
Stakeholders' Short-term Expectations
Today's market competitiveness has encouraged companies to focus on short-term profit maximization considering the economic profit concept. Stakeholders have given more emphasis on the bottom-line economic profit of the business. The core business is aligned to profit maximization objectives rather than sustainable business growth.
The current economic environment has also created more limitations on management in respect of implementing sustainable concepts. Most companies have misapplied the Triple Bottom Line concept as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), considering only the economic benefits. Leadership faces challenges matching these short-term profit objectives along with long-term sustainability standards.
Resistant Mindset to Change
Traditional and legacy organizational structures have created significant pressure on leadership to make changes in processes. These structures have established ways of doing things that may not align with today's needs for innovation, technological advancements, and organizational agility. This has resulted in the loss of competitive advantage in the long run.
Business sustainability efforts are continuous and evolutionary, requiring companies to be open-minded when dealing with change. Strategic, tactical, and long-term operational decisions need to meet the needs of today without negatively impacting the future.
Resource Allocation Challenge
Business resource allocation is a critical aspect involving the distribution of money, time, personnel, and material resources over various projects to achieve business goals effectively. The cost-of-living crisis, disrupted supply chains for food and energy, and cyberattacks have disrupted resource allocation decisions over sustainable practices (Global Risks Report, 2024).
These factors have created dilemma situations for business leaders at the time of resource allocation decisions. The focus on adequate resource allocation for sustainable initiatives — such as innovative technologies, employee training, social and environmental projects — may be missed due to these conflicting scenarios.
Less Focus from Regulatory and Compliance Authorities
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs), the Paris Agreement (signed in 2016), ESG Regulations, and various governmental and non-governmental organizations have brought regulations and frameworks to implement sustainable standards and goals.
However, authorities have given less priority or no major initiatives for the real implementation of sustainability practices. This has also resulted in the inability of seeing the economic and strategic benefits integrated in social and environmental values due to political agendas. Hence, business leaders are in a conundrum situation when interpreting and applying these requirements.
Measuring and Reporting Challenges
Integration of sustainability into accounting is a real challenge, especially relating to social and environmental reporting. Profits are measured in dollars — the question is: how do we measure social and environmental capitals? Currently, companies are using various measurement indexes and regulations such as the Dow Jones Sustainability Index, Bloomberg SRI Index, and Morgan Stanley Capital International Index.
Due to voluntary disclosure requirements, the importance and value of reported information are diluted. Further, AI-generated misinformation and disinformation are damaging accurate measuring and reporting information.
Leadership Blueprint
Leaders should focus on creating a balanced approach where economic success is achieved alongside positive social and environmental impacts, ensuring that the business contributes to a sustainable future. Building a robust solution by focusing on the following factors would lead to achieving sustainable growth of the business.
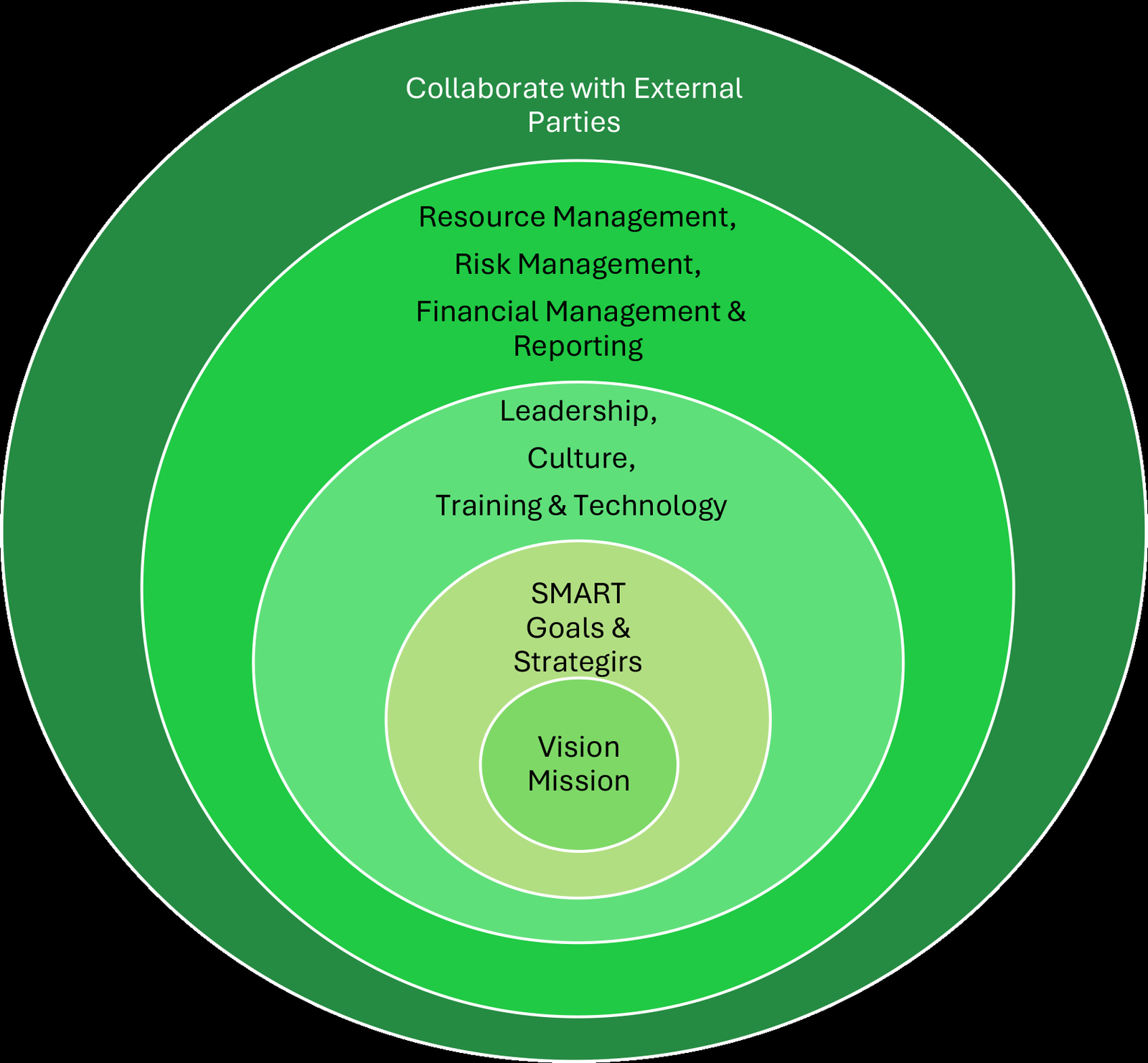
Blueprint Model for Sustainable Business Growth — Source: Author
Alignment of Company Vision and Mission with Sustainable Goals
Positive vision and mission statements emphasize management's commitment to achieving long-term organizational existence. Leaders should focus on embedding social and environmental factors along with economic benefits when establishing these statements.
As an example, the Tesla mission statement is to "accelerate the advent of sustainable transport by bringing compelling mass market electric cars to market as soon as possible." This statement provides a high-level commitment from company leaders to develop environmentally friendly electric cars for society.
SMART Goals and Strategies Focusing on Sustainable Growth
"All our dreams can come true, if we have the courage to pursue them" — Walt Disney. SMART goals and strategies help pursue the company's vision and mission to reality. Management should move beyond legacy systems and develop business models linked with SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound) objectives.
Management strategies — operational, sales and marketing, human resource, and financial management — should focus on developing sustainable business concepts. Top management commitment to sustainability should be considered when developing these business strategies with stakeholder involvement. These strategies will guide management to focus on the sustainable future of the business.
Leadership, Culture, Training and Technology
Top management commitment, governance structure, strong ethical policies, measurement and rewarding structures, and stakeholder involvement create the baseline for sustainable business growth success. Leadership integrity is one of the critical factors — leaders should be honest, truthful, and straightforward in personal and professional life, which brings roads to business success.
Today we deal with multicultural environments and various cultural factors that should be embedded into organizational structures. Core values aligned with cultural dimensions — such as employee recognition, customer satisfaction, customer relationships, and social responsibility — will help increase shareholder wealth and business growth.
Training and development are crucial to articulate all these factors within the organizational structure. Positive attitudes, behaviors, and leadership characteristics can be developed through various education and training programs.
Companies must bring innovative sustainable models to survive in future markets. Innovative sustainable thinking in business — such as Elon Musk's Tesla inventions — has resulted in boosting organizational performance in a short time span, becoming one of the most growing brands in the world.
Resource Management, Risk Management, Financial Management and Reporting
Top management should develop responsible and accountable organizational structures and system controls for efficient and effective resource management. Human resources, financial resources, materials, and time are critical to manage for optimal output. Resource management models, software, and AI-generated tools will help with planning, organizing, monitoring, and controlling resources.
Risk management aspects are important to minimize resource wastage, compliance issues, and reputation damage. Risk identification, analysis, evaluation, consultation, and monitoring processes help prepare for potential challenges. Simulation analysis, scenario analysis, heat maps, root cause analysis, matrices, and templates can be used to integrate the risk management process.
The best collection of data and reporting of sustainability relating to all three aspects of the TBL will grant the company an immense competitive advantage. Development and application of a unique integrated measurement, reporting, and rewarding system at the international level is important to govern the application of the sustainability concept.
Collaborate with External Parties
Business sustainability efforts are continuous and evolutionary, requiring companies to be open-minded when dealing with change. Businesses can drive more significant and impactful sustainability outcomes through strategic partnerships, resource sharing, and joint projects with shared goals.
Investment in renewable energy sources, recycling of waste, reforestation programs, energy conservation, employee well-being programs, and various community impact and social benefit programs show corporate commitment to sustainability. Businesses alone cannot resolve the sustainability challenges facing the world — social partners and stakeholders must be involved at the global level for long-term sustainability.
Forward Looking
Encouraging rewards for innovation would lead to competitive advantage and success in the corporate journey towards sustainability. Elon Musk's innovations and differentiations — such as Tesla Electric Cars, SpaceX, SolarCity, Solar Gigafactory, and Electric Jets — have created significant sustainable growth prospects for the future world.
Sustainability has become the paradigm for organizational success by balancing three aspects of economic, social, and environmental goals. Multinational Companies (MNCs) play a vital role in this task. Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) also have commitment, transparency, accountability, and responsibility toward this task. Companies like Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, and Google have significantly increased sustainable activities and reporting in recent decades.
International credit rating agencies also assign significant weight to social and environmental factors in their rating decisions. This can be considered a turning point for leaders to implement sustainability frameworks. Future growth of business will significantly depend on business leaders' evolutionary commitment and innovative response to sustainable practices.
References
- Bruntland Report (1987): Our Common Future, Report of the World Commission for Environment and Development, WCED, New York (NY).
- Kotter, J. P. (2007) Leading Change. Harvard Business Review, Jan 59-62.
- Virakul, B. (2015), "Global challenges, sustainable development, and their implications for organizational performance," European Business Review, Vol. 27 No. 4, pp. 430-446.
- World Economic Forum. (2024). The Global Risks Report. World Economic Forum.
- Tesla (2024): About the Company. Retrieved from https://www.tesla.com/about
FCA, MBA (Merit), B.Sc. (Accounting), ACMA, ACPM. Finance professional specializing in sustainable business growth and leadership strategy.
Stay Updated
Get the latest tutorials and articles delivered to your inbox.
No spam, ever. Unsubscribe anytime.


